Image Registration
• Thin-plate spline (TPS) deformable image registration
• B-spline deformable image registration
• Finite element model-based deformable registration
• Two-dimensional (2D) image registration software
• Three-dimensinal (3D) image registration software
• 3D to 2D Registration
• Slice to Volume Registration
Slice to volume registration is used to register a two-dimensional image slice to a three-dimensional image volume. In this study, we registered live-time interventional magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) slices with a previously obtained, high resolution MRI volume which in turn can be registered with a variety of functional images, e.g. PET and SPECT, for tumor targeting. We created and evaluated a slice-to-volume registration algorithm with special features for its potential use in iMRI-guided, radiofrequency (RF) thermal ablation. The algorithm features included a multi-resolution approach, two similarity measures, and automatic restarting in order to avoid local minima. Imaging experiments were performed on volunteers using a conventional diagnostic MR scanner and an interventional MRI system under realistic conditions. Both high-resolution MR volumes and actual iMRI image slices were acquired from the same volunteers. Actual and simulated iMRI images were used to test the dependence of slice-to-volume registration on image noise, coil inhomogeneity, and RF needle artifacts. To quantitatively assess registration, we calculated the mean voxel displacement over a volume of interest between slice-to-volume registration and volume-to-volume registration, which was previously shown to be quite accurate. More than 800 registration experiments were performed. For transverse image slices covering the prostate, the slice-to-volume registration algorithm was 100% successful with an error of < 2 mm, and the average and standard deviation was only 0.4 mm ± 0.2 mm. Visualizations such as combined sector display and contour overlay showed excellent registration of the prostate and other organs throughout the pelvis. Error was greater when an image slice was obtained at other orientations and positions, mostly because of inconsistent image content such as that obtained from variable rectal and bladder filling. These preliminary experiments indicate that MR slice-to-volume registration is sufficiently accurate to be able to aid image-guided therapy.
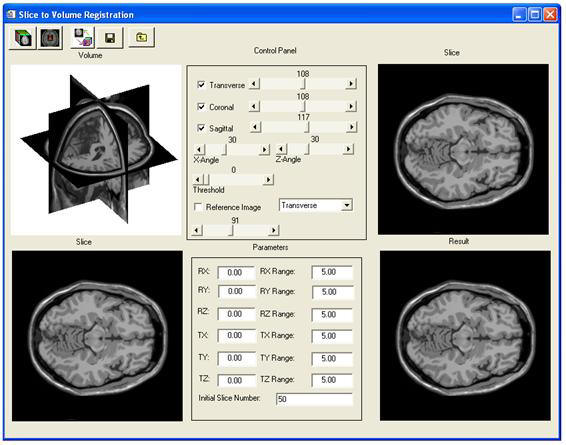
Figure 7. The slice to volume registration software.
Image ClassificationImage Segmentation
Attenuation Correction
Partial Volume Correction
Motion Correction